Drives
Label Volume
▶ Drive – Label
With this function you can assign a label to a drive. Depending on the data carrier type, the length of this designation is limited to 32 or 11 characters.
NOTE: Operation Center may need to be run as an administrator to assign a label to a drive.
Format Drive
▶ Drive – Format
You can use this function to format a drive or data carrier. Some brand new data carriers require formatting before they can be used.
NOTES:
1) When formatting, all data that may be present on the selected drive or data medium will be deleted!
2) Do not close Operation Center until formatting is complete.
Copy Drive
▶ Drive – Copy
This function allows you to create copies of a drive.
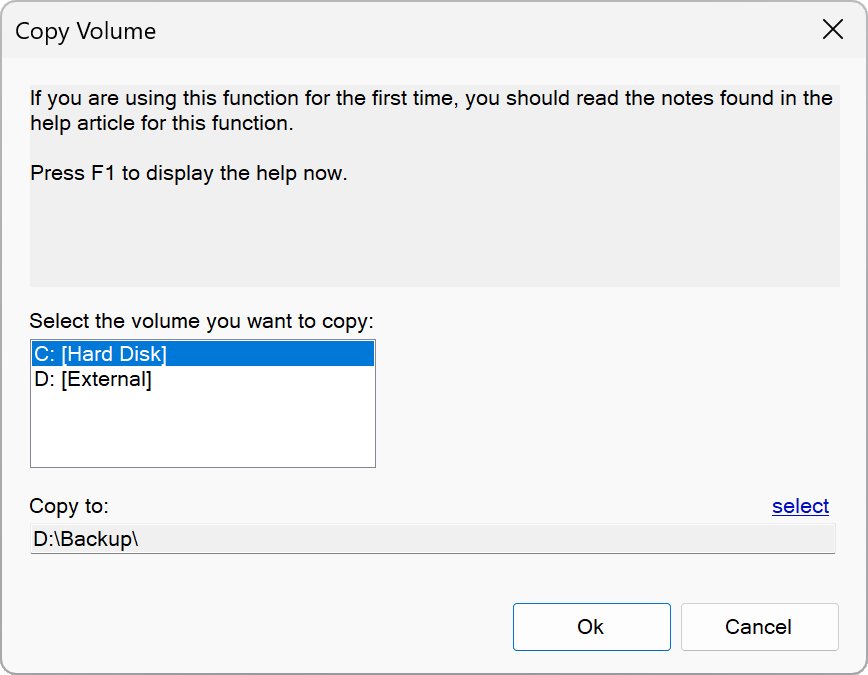
Please read the following notes if you use this function for the first time:
1) Ensure that the destination drive has enough free space, before you begin copying.
2) Files that are currently in use by another application may not be copied. Therefore we recommend to close all other applications before starting the copy process.
3) When copying a hard disk the recycle bin folder “$RECYCLE.BIN” will not be copied due to technical reasons.
4) When copying from a hard disk drive to a USB drive or USB stick the copy process may slow down over the time. This problem is often caused by the hardware or drivers used and not by Operation Center.
5) If the source drive contains very long path names and/ or highly convoluted folders, you should choose a short destination name on the destination drive, e. g. “C:\Copy\” – or shorter. Because if the maximum path length allowed by the file system is exceeded the affected files will not be copied from the source drive.
Open this Folder as a Drive
▶ Drive – Open this Folder as a Drive
With the help of this wizard you can assign a drive label to any folder. The contents of the folder and its subfolders are then also available under the assigned drive letter.
The drive will remain until the next restart of the PC.
Analyse Memory Allocation
▶ Drive – Analyse Memory Allocation
Analyses and displays the memory allocation of the selected drive.
Drive Cleanup
▶ Drive – Cleanup
You can use this function to clean a drive of files that are no longer needed, such as temporary swap files (*.tmp), automatically created backup copies (*.bak), and ChkDsk file fragments. This frees up disk space.
Additional cleanup destinations are available for the system drive: browser caches, downloads, and the temp folder.
We recommend that you close all other applications before proceeding. After the search process is complete, you will get a list of all found files that match the specified pattern.
Check this list carefully! If you do not want certain files to be removed, uncheck the box in front of the respective file name. Click “Finish” to remove all selected files.
It may not be possible to remove individual files if they are currently being used by another application or if sufficient user rights are missing.
Map Network Drive
▶ Drive – Map Network Drive
This section explains how to access another PC. It must be within the same network or connected to the same router.
Share a desired folder on the PC that you want to access:
1. Launch Windows Explorer
2. Right-click on the folder you want to share
3. Select “Properties”
4. The “Properties” window opens. Select the “Sharing” tab here
5. Click on “Share...”
6. Select the users you want to give access
7. Click “Share”
Now the folder should have been shared on your network.
Under “The folder has been shared” you can see the network path to the folder, e.g.:
\\MY-DESKTOP\My-Folder\
Now go to another PC from which you want to access the shared folder:
1. Launch Operation Center
2. Select “Drive – Map Network Drive...”
3. Select a drive letter for the drive (e.g. “Z:”)
3. Enter the above network path to the shared folder, e.g.:
\\MY-DESKTOP\\My-Folder\
4. Click “Finish”
After the successful connection, you will be able to access the folder that is located on the other PC.
It can be reached under the specified drive letter (e.g. “Z:”).
HINT:
If the other PC is turned off or unreachable, Operation Center and other applications may become sluggish. Disconnect the network drive if you don't need to access it for a longer period of time.
Safely Remove Drive
▶ Drive – Safely Remove
This function allows you to safely remove connected devices, such as USB sticks or USB hard drives, from your PC.
If you simply disconnect a connected device from your PC during operation without first removing it safely, data loss can occur.
Check Drive
▶ Drive – Check
You can use this function to check a drive or data medium for errors.
Please note that a check may take some time if the option “Search for bad sectors” is activated. A simple test, on the other hand, often only takes a few minutes.
Because optical storage media (CD, DVD and Blu-ray) cannot be checked with CHKDSK, the Operation Center provides a separate routine for these media.
HINT:
Operation Center may need to be run as an administrator in order to scan a drive, especially if it is the system drive.
Optimise
▶ Drive – Optimise
Defragments a drive.
When you work with your PC, it slows down over time when files on a drive (especially the hard drive) are often changed. If a file is deleted, an unused block is arising on the data carrier. When a new file is later created that is larger than the previously deleted file, it is not saved in one piece, but stored on the drive in several parts – the previously unused block was smaller than the new file.
The user notices this indirectly through the gradual slowdown of the drive. With the help of defragmentation, the drive is optimised and files are stored in one piece again. This will bring it back to its original speed.
🠈
